
Monochasial scorpioid lateral branches so that flowers are crowded around the Two opposite lateral sessile cymes at the axil of the node,each of it produces Pedicellate cymes, (simple or compound dichasia). Racemose and cymose patterns of development occur in a mixed manner. Sympdial Cyme : In monochasial cyme, successive axesĪt first develop in a zigzag manner and later it develops into a straight Polychasial Cyme (multiparous ): The central axis ends with a flower. Example: Clerodendron.Ī small,simple dichasium is called cymule Each compound dichasium consists of seven flowers. A terminal old flower develops lateral simple dichasial cymes onīoth sides. Example: Heliotropium.Īxis ends in a terminal flower further growth is produced by two lateral buds.Įach cymose unit consists of three flowers of which central one is old one.Ĭompound dichasium : It has many flowers. Scorpioid: Axis develops on alternate sides and often becomes a coil structure. Helicoid: A xis develops on only one side and forms a coil structure atleast at the earlier development From two lateral bracts, only one branch grows It may be terminal orĪxis ends with a flower. Old flowers present at apex andĬyme ( solitary) : Determinate inflorescence consists of a single flower. Tubular and bisexual whereas the ray florets found at the margin of theĬentral axis stops growing and ends in a flower,įurther growth is by means of axillary buds. Head : The inflorescence possesses both types of Example: Vernonia, Ageratum or Ray florets alone. A group of bracts presentīeneath the sub unit of inflorescence is known as Involucel. Such whorl of bracts is called involucre. That the whorl of bracts forms a cup like structure beneath mimicking theĬalyx. Subtended by a lateral appendage called bract. Nilotica, Albizia lebbeck, Mimosa pudica (sensitive plant). Indeterminate, group of sessile or sub sessile flowers arising on a receptacle,Īsteraceae and is also found in some members of Rubiaceae.
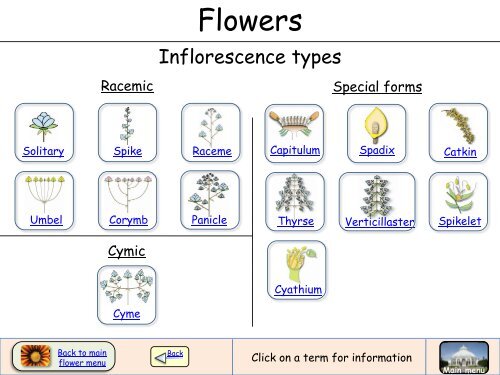
The main axis of inflorescence is mostly flattened Example: Daucas carota, Coriandrum sativum, Memecylon Example: Allium cepa, Centella asiatica, Memecylon umbellatum. Example: Cauliflower.Ĭentral axis and pedicellate flowers arise from a common point of peduncle at Compound corymb: A branched corymb is called compound corymb. Pedicellate flowers at the top and longer pedicellate flowers at the bottom.Īll flowers appear at the same level to form convex or flat topped racemose


There are two types namely corymb and umbel. Inflorescence with reduced growth of central axis. It is also called Compound raceme or raceme of racemes. Example: Amorphophallus, Colocasia, Phoenix, Cocos. Entire inflorescence is covered by a brightly coloured or hard bract called a spathe. Usually female flowers are found towards the base and Įxample: Acalypha hispida, Prosopis juliflora, Piper nigrum.įleshy or thickened central axis that possesses many unisexual sessile flowers Catkin : Pendulous spikes with a long and drooping axis bearing small Example: Paddy, Wheat, Barley, Sorghum.ĭ. Tepals reduced to colourless scaly leaves (lodicule). Each sessile flower has a lemma (bract) and a palea Pair of inflorescence bracts called glumes Sessile flowers are formed in acropetal succession on the axis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
